Complete Guide to Earthing Systems: Copper Earthing, GI Earthing, Chemical Earthing & Earthing Safety
Earthing is the backbone of electrical safety, protecting people, equipment, and infrastructure from electrical faults and lightning strikes. This guide explains Copper Earthing, GI Earthing, Chemical Earthing, and covers important aspects like Earthing Safety, comparing materials and components used in modern earthing systems.
Enquiry Form
1. Earthing Safety
Earthing Safety is critical to prevent electrical shock hazards, fire, and equipment damage. A well-designed and maintained earthing system ensures fault currents are safely dissipated into the ground. Regular testing, corrosion checks, and adherence to standards are essential for safety.
Key takeaway: Without proper earthing safety measures, electrical systems can be extremely dangerous.
2. Copper Earthing
Copper Earthing uses copper rods and electrodes as grounding elements. Copper is preferred because of its:
-
Excellent electrical conductivity
-
High corrosion resistance
-
Long life span
-
Low maintenance requirements
Copper Rods
Copper Rods are long, slender, copper-coated steel rods that are driven into the ground. They serve as the main conductor to earth, providing a low-resistance path for fault currents.
Copper Electrodes
Copper Electrodes are the actual contact points buried in the earth, often copper-bonded rods or plates, designed to maintain consistent electrical conductivity.
Copper earthing is ideal for reliable and long-lasting grounding solutions.
3. Copper Benefits
Copper’s properties make it the most reliable earthing material. Its benefits include:
-
Superior conductivity ensuring minimal resistance
-
Resistance to rust and corrosion, even in harsh soil conditions
-
Durability leading to reduced replacement and maintenance costs
-
Stability in performance over many years
Copper’s high efficiency ensures safety and reliability for electrical systems.
4. Copper vs GI Earthing
The debate between Copper vs GI Earthing centers on cost, durability, and performance:
| Aspect | Copper Earthing | GI Earthing |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Limited; prone to corrosion |
| Maintenance | Low | Requires frequent inspection |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Lifespan | Longer (20+ years) | Shorter (5-10 years) |
Copper earthing is recommended where durability and performance are critical, while GI earthing suits budget-conscious projects.
5. GI Earthing
GI Earthing uses galvanized iron (GI) rods and strips as grounding components. Zinc coating on GI products helps resist corrosion temporarily.
GI Earthing Rods
GI Earthing Rods are steel rods coated with zinc to delay corrosion and provide a conductive earth path.
GI Earthing Strips
GI Earthing Strips are flat, flexible, zinc-coated steel strips used to connect rods and electrical systems.
6. GI Earthing Benefits
GI Earthing provides:
-
Cost-effective grounding solutions
-
Good mechanical strength and flexibility
-
Easy availability and installation
Despite its lower durability compared to copper, GI earthing is widely used for its affordability and performance in less corrosive soils.
7. GI Earthing Safety
GI Earthing safety depends on regular maintenance because zinc coating can wear off, leading to increased resistance and potential faults. Ensuring secure connections and routine checks are vital to maintain safety.
8. GI Earthing Systems
A complete GI Earthing System consists of rods, strips, clamps, and connectors assembled to provide a safe grounding network. Design and installation must comply with electrical safety standards for effective operation.
9. GI Earthing Solutions
Custom GI Earthing Solutions are designed considering soil resistivity, moisture, and environmental factors to optimize earthing performance in different conditions.
10. GI Earthing Installations
Professional GI Earthing Installations involve correct placement, depth, backfilling with suitable materials, and periodic testing to maintain earth resistance at safe levels.
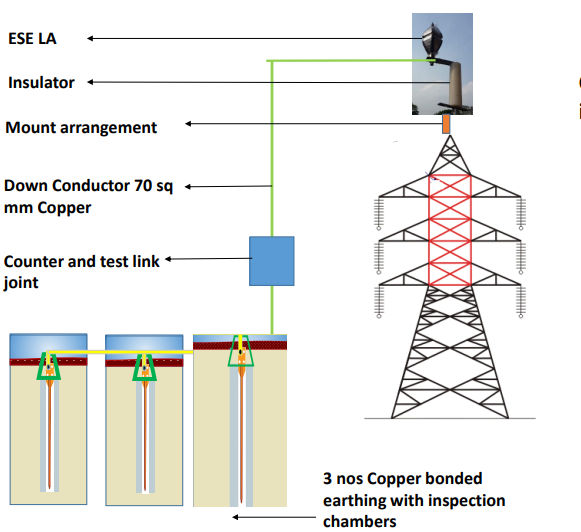
11. Chemical Earthing
Chemical Earthing enhances soil conductivity by embedding electrodes (copper or GI) in conductive chemical compounds, like bentonite, graphite, or salt mixtures.
How Chemical Earthing Works:
-
Chemical compounds retain moisture and improve soil conductivity
-
Reduce earth resistance significantly even in dry or rocky soil
-
Protect electrodes from corrosion
-
Provide stable and low-resistance grounding path
Applications
Chemical earthing is widely used in high soil resistivity areas, power distribution, telecom towers, and lightning protection systems.
Conclusion
Choosing the right earthing method depends on application requirements, soil conditions, and budget. Copper Earthing offers superior performance and longevity, while GI Earthing provides cost-effective solutions. Chemical Earthing is essential in challenging soil environments to maintain reliable grounding.
Remember, Earthing Safety is paramount regardless of the system used. Regular maintenance and testing ensure long-term protection and reliability.
At Arete Powertech, we provide high-quality earthing products including Copper Rods, Copper Electrodes, GI Earthing Strips, GI Earthing Rods, and advanced Chemical Earthing solutions to meet all your grounding needs.